BYD Blade Battery : The turning point innovation in electric vehicle batteries. The best innovation that changes the world.

The BYD Blade Battery is an innovation in battery technology developed by BYD Auto Co., Ltd., a Chinese company that manufactures electric and hybrid vehicles. This type of battery is renowned in the electric vehicle technology industry for its unique design features and high safety standards making it popular in the global electric car market.
The distinctive feature of the BYD Blade Battery is the arrangement of battery cells in a blade-like formation which increases the contact area between cells and electrical pathways resulting in efficient heat transfer. Additionally, this unique design helps reduce the risk in the event of a vehicle collision. The BYD Blade Battery has been continuously integrated into BYD electric vehicles making it a technology with significant implications for the global electric car industry standards.
Topic
Introducing the BYD Blade Battery
BYD previously entered the Thai market, initially in collaboration with Loxley Public Company Limited, bringing the E6 model and K9 buses to the market. However, it gradually faded away. Subsequently, BYD partnered with AJ Advance Technology Public Co., Ltd. and Charich Holding Company Limited, introducing the E6 as taxis for a period before disappearing again.
Recently, BYD has returned to garner attention with the announcement of Rêver Automotive as the official distributor under the leadership of Prathanwong Phonplapa and Prathanphon Phonplapa. This comeback marks Rêver Automotive’s goal to drive the country towards becoming an NEV (New-Energy Vehicle) technology and innovation, a commitment to pushing for Net Zero Emission in Thailand.

For the car brand BYD, it was founded in China with the name BYD derived from shortening the phrase ‘Build Your Dreams’ to simply ‘BYD’. Initially, BYD was a company involved in battery and electrical appliance businesses. Later, it ventured into the automotive industry, covering the manufacturing of cars, buses, trucks, and forklifts as well as integrating knowledge from the battery industry into cars. This shift came after the Chinese government’s policy to promote electric cars. Shortly thereafter, BYD started producing plug-in hybrid electric vehicles and eventually fully electric cars.

Afterward, BYD once again made global headlines when rumors surfaced that Tesla, the American electric car company, wanted them to produce batteries. This was because BYD had successfully developed a new type of battery called the Blade Battery, which uses Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and has passed the standard Nail penetration test. In this test, a nail is driven through the center of the battery cell until it penetrates to the other side, causing a short circuit inside the battery cell. Through this testing, BYD’s Blade Battery demonstrated higher safety standards compared to Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide batteries.

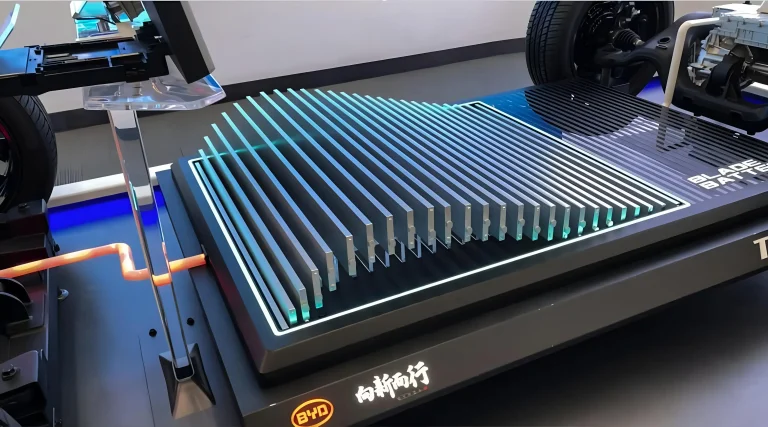
Therefore, BYD’s Blade Battery boasts a high level of safety in cases of severe battery damage. Additionally, its design resembles that of a blade, making it thinner and longer than conventional batteries. This design enables BYD batteries to dissipate heat more quickly than typical rectangular cell batteries. In the event of a short circuit within a cell, it does not affect other cells, thus preventing continuous electrical short circuits. Furthermore, the Blade Battery is designed using cell-to-pack technology (CTP) where each cell can be directly packed without the need for module packing, allowing for more cells to be added.
Moreover the Blade Battery can also serve as a structural reinforcement material for vehicle frames further enhancing their strength. These highlighted features demonstrate the safety standards of the Blade Battery from the BYD brand.
Limitations of electric vehicles (EVs)
The limitations that have hindered the widespread use of electric vehicles (EVs) in the past are mainly related to the performance of the vehicle’s batteries. These include inadequate driving range per single charge (typically averaging around 250-400 kilometers / single charge) , insufficient coverage of charging stations across the country, and longer charging times compared to refueling conventional gasoline cars. There have also been safety concerns regarding battery performance in the event of collisions or severe impacts.
However, in the year 2021, the world became acquainted with the term ‘Blade Battery,’ which even caught the attention of Elon Musk, who considered incorporating this type of battery into Tesla cars. The standout feature that makes the ‘Blade Battery,’ patented by BYD, a sought-after innovation among EV manufacturers.
The advantages of the BYD Blade Battery.
The two main advantages of the BYD Blade Battery which EV manufacturers aim for and are exclusive to BYD
1. Lower production costs with lower heat generation but higher energy storage capacity.
The Blade Battery uses Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) which has undergone standard testing through the Nail penetration test method. In this test a nail is driven through the center of the battery cell until it penetrates to the other side causing a short circuit inside the battery cell. Through this testing, BYD’s Blade Battery has demonstrated higher safety standards compared to Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide batteries. Additionally, it also has lower production costs compared to NMC (Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide) battery production costs referenced to the price of nickel as the basis for NMC battery production costs.
2. Safety Superiority in Case of Accidents
According to safety standards the LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery type in BYD Blade Battery has higher safety standards than NMC and NCA due to its higher decomposition temperature (approximately 270 degrees Celsius), while other battery types are around 210 and 150 degrees Celsius respectively. Additionally, when damaged it releases less heat compared to other battery types.
With the proven quality of this Blade Battery innovation all issues are resolved, including cost, efficiency, and safety concerns. Therefore, its usage is increasingly popular with more charging stations being established especially in Thailand where there is growing awareness of EVs and a significant increase in charging stations.
The turning point in the electric vehicle (EV) battery industry
As widely known governments in many countries have increasingly supported the domestic use of electric cars. Policies such as reducing import taxes on electric cars or providing subsidies for purchasing them have been implemented to encourage the populace to adopt electric cars more readily. This is because governments have recognized the need to reduce the use of internal combustion engines within the country and to address environmental issues caused by emissions from Internal Combustion Engine vehicles.
However, the increase in the adoption of electric cars by the populace is not without its challenges, as electric cars still face several limitations, including:
- The inadequate driving range per single charge (typically averaging around 250-400 kilometers per single charge)
- Insufficient coverage of charging stations across the country or longer charging times compared to refueling conventional gasoline cars.
- Safety concerns regarding the batteries in electric cars in the event of collisions or severe impacts.
It can be observed that most of these major issues are directly related to the performance of batteries in electric vehicles. In the past year leading Chinese battery and electric vehicle manufacturers like BYD have introduced a new type of car battery called the “Blade Battery.” This battery has gained widespread attention in 2021-2022, being touted as a game-changer in the electric vehicle industry. Even Elon Musk has shown interest in incorporating this type of battery into the Tesla Brand.
How is BYD’s new Blade Battery better than the previous LFP batteries? And what changes can this type of battery bring to the electric vehicle industry?
1. Safety measurements that surpass those of general
To truly understand this matter we need to familiarize ourselves with the types of electric vehicle (EV) batteries and the chemicals contained within each type. If we were to categorize EV batteries in the market based on the type of chemicals they contain, we can divide them into three types Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC), Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA), and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP).In terms of energy density typically NMC batteries have higher efficiency than LFP batteries. However, when it comes to safety standards, LFP batteries have higher safety standards than NMC and NCA batteries because they have a higher decomposition temperature, approximately 270 degrees Celsius, while NMC and NCA batteries have decomposition temperatures of approximately 210 and 150 degrees Celsius respectively. This higher safety standard of LFP batteries comes from the fact that when damaged, they release less heat approximately 200 J/g, whereas NMC and NCA batteries can release up to 600 and 900 J/g of heat respectively.Therefore, BYD’s new Blade Battery chooses to use chemicals that are LFP-based inside ensuring higher safety standards.

Image : Table Showing Safety Properties of Chemicals in NMC, LFP, and NCA Car Batteries (Source: Article “Risks Associated With Lithium: Can You Really Trust A Lithium Battery?“)
When it comes to testing the safety standards of electric vehicle (EV) batteries the Nail penetration test method must be mentioned as it is considered one of the most challenging tests. The nature of this test involves driving a nail through the center of the battery cell until it penetrates to the other side, causing a short circuit inside the battery cell. This short circuit leads to rapid heat accumulation, a phenomenon known as Thermal runaway, ultimately resulting in a significant increase in surface temperature. Eventually, this can lead to combustion or explosion.In this test BYD’s Blade Battery demonstrates exceptionally high safety standards compared to NMC and LFP conventional batteries. When tested using the Nail penetration method BYD’s NCM battery exhibits clear signs of combustion and explosion with surface temperatures reaching as high as 500 degrees Celsius. On the other hand the conventional LFP battery does not show clear signs of combustion but emits visible smoke with surface temperatures ranging from 200 to 400 degrees Celsius enough to cook a raw egg. Conversely, BYD’s Blade Battery does not exhibit combustion or smoke emission characteristics. There is only a slight change in the surface temperature of the battery, ranging from 30 to 60 degrees Celsius. This indicates that there is almost no thermal reaction occurring during the Nail penetration test with BYD’s Blade Battery. Consequently, BYD batteries are considered highly safe in cases of severe battery damage.
VDO : The safety standard testing of batteries using the Nail penetration test method by BYD, which demonstrates a higher safety standard of the BYD Blade Battery compared to conventional NCM and LFP batteries. (Source: YouTube channel: Afriplus Energy by BYD Premium Channel “BYD blade battery nail penetration test“)
What makes BYD’s LFP battery superior to the safety standards of conventional LFP batteries is the design of the battery cells, including the arrangement and shape of the battery cells. The shape of BYD’s battery cells is designed to resemble a blade, hence called the “Blade” battery. They are thin and elongated, unlike conventional batteries that are stacked and have a blocky appearance. This design allows BYD’s battery cells to have a significantly higher surface area for heat dissipation, enabling them to dissipate heat rapidly compared to rectangular block-type battery cells. Additionally, the arrangement of battery cells in a configuration similar to a heat sink ensures clear separation between battery cells and provides ample space for airflow between the battery cells. In the event of a short circuit within a cell or heat accumulation, it becomes difficult for the heat or electrical short to propagate to neighboring battery cells, minimizing the risk of continuous electrical shorts. Consequently, the occurrence of explosions or fires becomes relatively challenging.
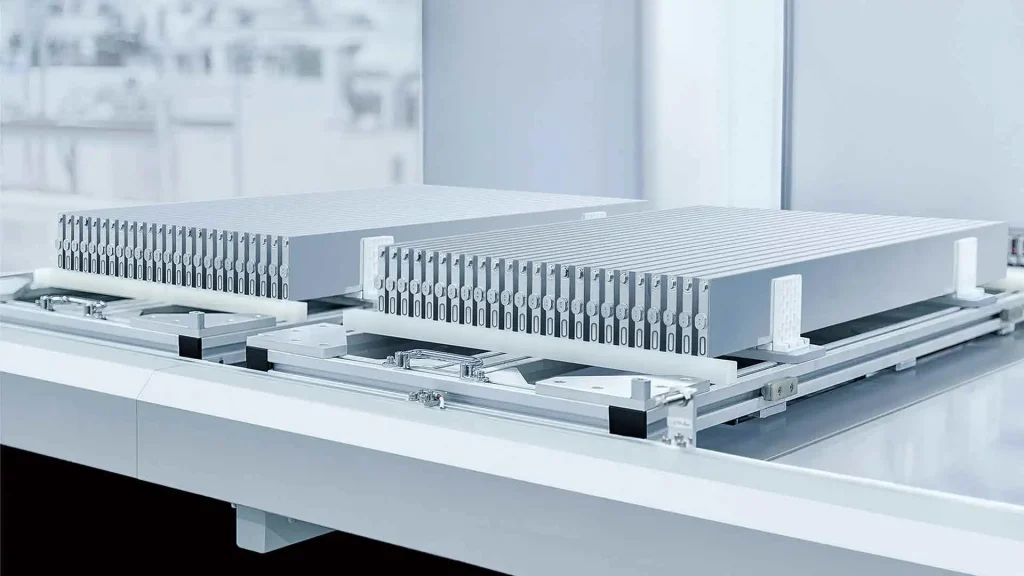

Photo : The characteristics of the car battery cells of BYD Blade Battery and the arrangement of battery cells that resemble the features of a heat sink in computer devices.
(Soure : Article on “BYD Shows Off New Blade Battery Factory In Chongqing“)
2. Energy density that stands out with module-free technology
Due to the fact that BYD’s Blade Battery is designed with cell-to-pack technology (CTP) which results in a relatively high energy density. Generally, conventional batteries have battery cells packed into modules first, and then each module is packed into battery packs. However, this conventional packing method consumes a significant amount of space to accommodate the battery cells since each module needs additional materials to facilitate module replacement in case of battery degradation. Therefore, the volumetric cell-to-pack ratio (VCTPR) in conventional batteries is relatively low, around 50% or even lower at 40%. In contrast, BYD’s Blade Battery allows each battery cell to be packed directly without the need for module packing (module-free), which increases the space available for adding more battery cells. With the ability to increase the number of battery cells, the energy density of the battery also increases accordingly. Moreover, besides the advantage of capacity, BYD’s Blade Battery can also be used as structural reinforcement for vehicles. With the cells of the Blade Battery being uniform and directly packed into battery packs, they can withstand significant pressure applied from above or in the Z-axis direction. BYD conducted a test where a 46 ton truck was placed on top of the battery pack, and the results showed that the battery maintained its normal shape without any changes in temperature, allowing the tested battery to be reused in vehicles.
These two advantages demonstrate a high safety standard and superior energy density compared to conventional LFP batteries. Therefore, these significant reasons may lead to a shake-up in the electric vehicle battery industry, where many major automakers may turn to BYD’s batteries for use in their electric vehicles. In the future, we may see electric vehicles with high safety standards, where no fire or explosion occurs from the battery even in the event of a collision, and electric vehicles capable of traveling over 500 kilometers per charge at a price accessible to the general public, leading to more electric vehicles on the roads than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
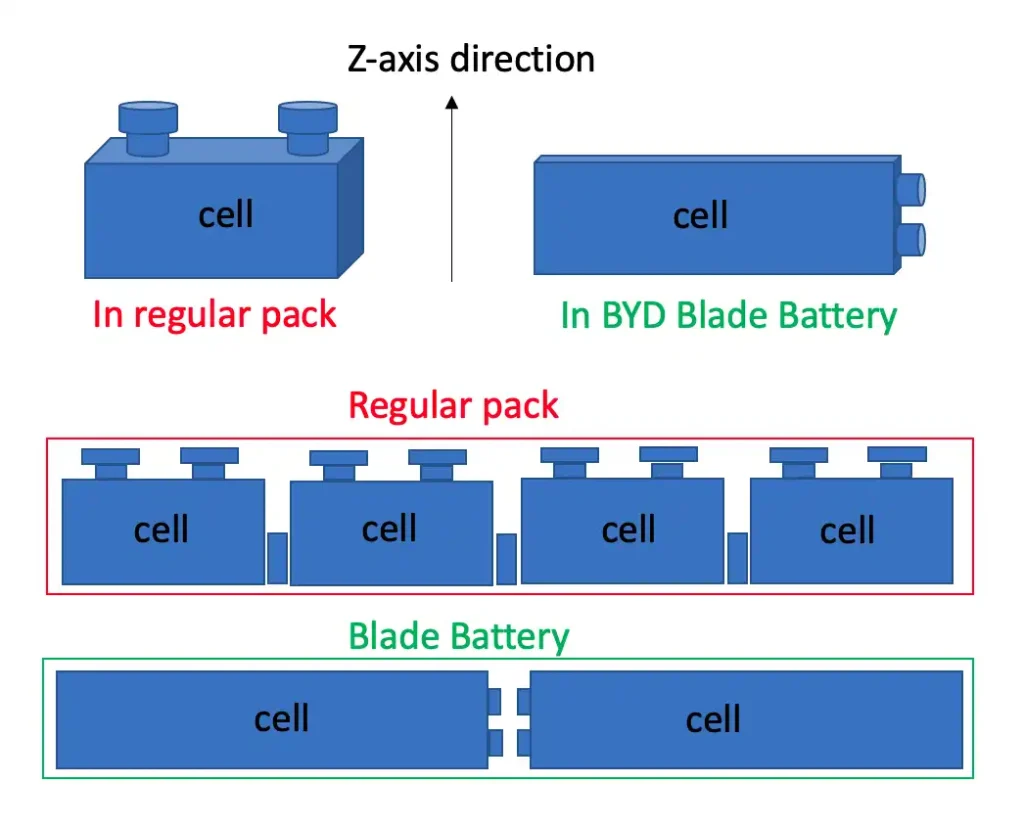
Photo : Module-free battery cell packing vs. traditional battery cell packing (left)
(Soure : Article on “The Next-Generation Battery Pack Design: from the BYD Blade Cell to Module-Free Battery Pack“)

FAQ
How many years does BYD battery last?
After 13 years of usage (1.2 million kilometers), the efficiency of the BYD battery will decrease by 20% based on the display screen. It means it can still operate at 80% capacity, and then gradually deteriorate depending on usage. If we purchase a new vehicle and no longer use the battery, it can be removed and utilized for storing solar energy.
What should I do if the battery charger at the electric vehicle charging station doesn’t work or the charging cable won’t detach?
When attempting to charge the battery at an electric vehicle charging station but encountering issues such as no power or difficulty in detaching the charging cable, you can follow these steps to troubleshoot
- Check the connection and locking of the charging head: Ensure that you plug in the charging head firmly and verify if it’s properly locked. If unsure about the locking mechanism, try unlocking the car and re-plugging the charging head to ensure it’s securely and correctly installed.
- Check for door locks (for some models): If your vehicle requires unlocking the doors before detaching the charging cable ensure that you have properly unlocked the car doors.
- Utilize the power cutoff switch on the charger unit: If you’re still unable to detach the charging head, try pressing the Emergency button or Off Breaker main to cut off power on the charger unit side. Afterward, you should be able to detach the charging head.
- Contact the Call Center of the electric vehicle charging station: If you’ve tried all the steps above and still can’t resolve the issue, it’s advisable to contact the Call Center of the electric vehicle charging station for technical assistance.
How can I check the quality of BYD batteries?
You can bring your vehicle for inspection at any BYD service center nationwide.
Contact Us
- Address : 607 Phetkasem Road, Kho Hong Subdistrict, Hat Yai District, Songkhla Province (BD Auto Group)
- Facebook : BYD BD Auto Group
- LINE : @bydbdsongkhla
- Branches of BYD BD Auto Group
- Songkhla (Hat Yai)
- Trang
- Narathiwat
- Thungsong
- Phuket
- Phuket (Bypass)
- Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Krabi
- Phone Number : 074 805 656 (Hat Yai Branch)
- Website : www.bydbdautogroup.com




